 产品分类 产品分类 友情链接 友情链接 |
|
首页 > 供应产品 > SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统
一、系统介绍SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统是一套通过视频摄像机和计算机,采用图像处理技术,自动跟踪和记录动物活动的通用型运动轨迹记录分析系统,可以应用在神经药理,学习记忆药理,药理和新药神经系统一般药理毒理研究,也可用于神经科学基础研究。SuperMaze适用于Morris水迷宫实验、开场实验、旷场实验、自发活动、避暗实验、T型迷宫、Y型迷宫、放射型迷宫、高架十字迷宫、八臂迷宫、Barnes迷宫、条件位置偏爱实验、Zero迷宫、孔洞实验、跳台实验、新物体识别等各种动物实验。 SuperMaze除了具有自动跟踪记录动物活动轨迹的基本功能外,还具有通过事件记录器记录视频系统无法自动识别的各项动物行为事件、轨迹数据导入再分析、实验数据管理以及实时录像功能,并能够接收16路外部输入信号,控制12路外部输出信号,充分体现了自动化与灵活性相结合的优势。SuperMaze动物行为轨迹分析平台设置简单、操作灵活,具有很高的性能价格比。 nnecttype="rect" gradientshapeok="t" o:extrusionok="f">  二、平台特性 二、平台特性 可随心设计的平台区域图形(平台软件开放),开展各种行为学实验 可随心设计的平台区域图形(平台软件开放),开展各种行为学实验 稳定可靠的头、中、尾三点跟踪算法,甚至可以可识别果蝇幼虫 稳定可靠的头、中、尾三点跟踪算法,甚至可以可识别果蝇幼虫 可以对动物的主动行为、学习记忆、条件反射、反应性、被动行为中的各种行为学数据进行采集处理 可以对动物的主动行为、学习记忆、条件反射、反应性、被动行为中的各种行为学数据进行采集处理 的事件统计和分析功能,实验结果一目了然 的事件统计和分析功能,实验结果一目了然 可视化的实验数据管理功能,安全便捷 可视化的实验数据管理功能,安全便捷 强大的综合报表功能,并支持一键导出 强大的综合报表功能,并支持一键导出 灵活的实验启动和结束方式,提高实验效率 灵活的实验启动和结束方式,提高实验效率 内置方便快捷的手动事件记录器,记录动物各种行为特征 内置方便快捷的手动事件记录器,记录动物各种行为特征 自定义实验动物的属性模板 ,实验参数更丰富全面 自定义实验动物的属性模板 ,实验参数更丰富全面 软件扩展齐全,支持16通道的实验分析 软件扩展齐全,支持16通道的实验分析 控制器可以兼容国外行为学厂家仪器,技术国内三、实验开展1. morris水迷宫(Morris water maze, MWM) 控制器可以兼容国外行为学厂家仪器,技术国内三、实验开展1. morris水迷宫(Morris water maze, MWM) Morris水迷宫实验是一种强迫实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)游泳,学习寻找隐藏在水中平台的一种实验,Morris水迷宫主要用于测试实验动物对空间位置感和方向感(空间定位)的学习记忆能力,被广泛应用于学习记忆、老年痴呆、海马/外海马研究、智力与衰老、新药开发/筛选/评价、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学及行为生物学等多个学科的科学研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,在世界上已经得到广泛地认可,是医学院校开展行为学研究尤其是学习与记忆研究的经典实验。2. T迷宫实验(T-maze) T迷宫由1条干和2条臂构成。迷宫使动物在获取食物奖励时没有任何参考,只能根据自我判断选取食饵正确摆放一端。一般在测试前几天对其食量进行限制,测试前2天对动物进行训练。之后进行正式测试,每日连续测试15次,每次测试间隔1min,共3d。 Morris水迷宫实验是一种强迫实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)游泳,学习寻找隐藏在水中平台的一种实验,Morris水迷宫主要用于测试实验动物对空间位置感和方向感(空间定位)的学习记忆能力,被广泛应用于学习记忆、老年痴呆、海马/外海马研究、智力与衰老、新药开发/筛选/评价、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学及行为生物学等多个学科的科学研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,在世界上已经得到广泛地认可,是医学院校开展行为学研究尤其是学习与记忆研究的经典实验。2. T迷宫实验(T-maze) T迷宫由1条干和2条臂构成。迷宫使动物在获取食物奖励时没有任何参考,只能根据自我判断选取食饵正确摆放一端。一般在测试前几天对其食量进行限制,测试前2天对动物进行训练。之后进行正式测试,每日连续测试15次,每次测试间隔1min,共3d。 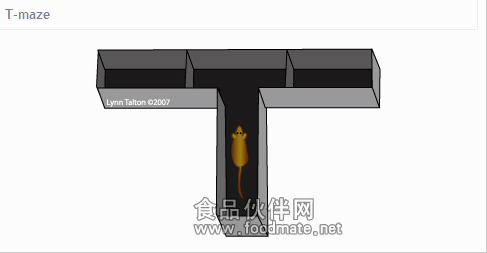 The T-maze is a choice task. The subject is placed in the base of the "T". Following a short delay, it is allowed to explore the maze and choose to enter either the right or left arms. The choice is scored according to variety of criterion, including spontaneous alternation, cued reward, or to indicate a preference. based on the criterion used in an experiment, the T-maze can be used to test learning and memory, preferences for stimuli or reward, or spontaneous alternation behavior.3. 八臂迷宫(Radial Arm Maze) Subjects are placed in the center of an eight-arm radial maze. Four randomly chosen arms are baited with food pellets in opaque containers. The subject is given the opportunity to visit all the arms and collect all the available food pellets. The T-maze is a choice task. The subject is placed in the base of the "T". Following a short delay, it is allowed to explore the maze and choose to enter either the right or left arms. The choice is scored according to variety of criterion, including spontaneous alternation, cued reward, or to indicate a preference. based on the criterion used in an experiment, the T-maze can be used to test learning and memory, preferences for stimuli or reward, or spontaneous alternation behavior.3. 八臂迷宫(Radial Arm Maze) Subjects are placed in the center of an eight-arm radial maze. Four randomly chosen arms are baited with food pellets in opaque containers. The subject is given the opportunity to visit all the arms and collect all the available food pellets.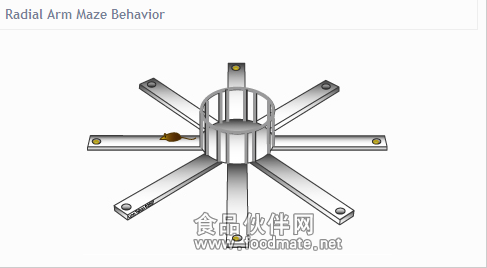 After a rentention delay, the subject is returned to the maze. In win-stay conditions, the same four arms are baited, and the number of correct choices the subject makes in collecting the pellets is recorded. In win-shift conditions, the four arms NOT baited in the earlier trial are now baited, and the number of correct arm choices is recorded. Each day, a new set of four arms is chosen randomly.八臂迷宫用来检测药物或大脑受损状态下学习和记忆方面的表现,它由八个完全相同的臂组成,这些臂从一个中央平台放射出来,所以又被称为放射迷宫每个臂尽头有食物提供装置,根据分析动物取食的策略即进入每臂的次数、时间、正确次数、错误次数、路线等参数可以反映出实验动物的空间记忆能力。相对而言,八臂迷宫操作简便、可行,而且能区分短期的工作记忆和长期的参考记忆,现已被广泛用于学习记忆功能评价。 4. 自主活动、旷场实验(Open Field) The subject is placed in the activity chamber for a specified time period. Activity levels and movement in three After a rentention delay, the subject is returned to the maze. In win-stay conditions, the same four arms are baited, and the number of correct choices the subject makes in collecting the pellets is recorded. In win-shift conditions, the four arms NOT baited in the earlier trial are now baited, and the number of correct arm choices is recorded. Each day, a new set of four arms is chosen randomly.八臂迷宫用来检测药物或大脑受损状态下学习和记忆方面的表现,它由八个完全相同的臂组成,这些臂从一个中央平台放射出来,所以又被称为放射迷宫每个臂尽头有食物提供装置,根据分析动物取食的策略即进入每臂的次数、时间、正确次数、错误次数、路线等参数可以反映出实验动物的空间记忆能力。相对而言,八臂迷宫操作简便、可行,而且能区分短期的工作记忆和长期的参考记忆,现已被广泛用于学习记忆功能评价。 4. 自主活动、旷场实验(Open Field) The subject is placed in the activity chamber for a specified time period. Activity levels and movement in three dimensions are recorded by the activity system and can be analyzed for evidence of hyperactiviy, hypoactivity, anxiety, explorative behaviors, and stereotyped rotation. 自发活动旷场旷场分析系统是观察研究实验动物神经精神变化、进入开阔环境后的各种行为,例如动物对新开阔环境的恐惧而主要在周边区域活动,在中央区域活动较少,但动物的探究特性又促使其产生在中央区域活动的动机,也可观察由此而产生的焦虑心理。中枢兴奋药物可以明显增加自主的活动而减少探究行为,一定剂量的抗精神病药物可以减少探究行为而不影响自主活动。5. 高架十字迷宫(Elevated Plus Maze) 高架十字迷宫是利用动物对新异环境的探究特性和对高悬敞开臂的恐惧形成矛盾冲突行为来考察动物的焦虑状态。高架十 dimensions are recorded by the activity system and can be analyzed for evidence of hyperactiviy, hypoactivity, anxiety, explorative behaviors, and stereotyped rotation. 自发活动旷场旷场分析系统是观察研究实验动物神经精神变化、进入开阔环境后的各种行为,例如动物对新开阔环境的恐惧而主要在周边区域活动,在中央区域活动较少,但动物的探究特性又促使其产生在中央区域活动的动机,也可观察由此而产生的焦虑心理。中枢兴奋药物可以明显增加自主的活动而减少探究行为,一定剂量的抗精神病药物可以减少探究行为而不影响自主活动。5. 高架十字迷宫(Elevated Plus Maze) 高架十字迷宫是利用动物对新异环境的探究特性和对高悬敞开臂的恐惧形成矛盾冲突行为来考察动物的焦虑状态。高架十 字迷宫具有一对开臂和一对闭臂,高架十字迷宫距离地面较高,相当于人站在峭壁上,使实验对象产生恐惧和不安心理。高架十字迷宫被广泛应用于新药开发、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学等多个学科的科学-研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,是医学院校与科研机构开展焦虑抑郁研究的经典实验。Xmaze 动物行为轨迹分析平台The animal is placed in the center of the apparatus and observed for a set time. Measurements compare the include total time spent in the open and closed arms (and central platform) as well as entries into the open and closed arms.6. 黑白箱实验(light dark box) The subject is placed in the dark portion of the box for a set period of acclimation time. At the end of this period, a door separating the two compartments is opened. The amount of time that the subject takes to emerge fully from the enclosed area into the open area is measured. 字迷宫具有一对开臂和一对闭臂,高架十字迷宫距离地面较高,相当于人站在峭壁上,使实验对象产生恐惧和不安心理。高架十字迷宫被广泛应用于新药开发、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学等多个学科的科学-研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,是医学院校与科研机构开展焦虑抑郁研究的经典实验。Xmaze 动物行为轨迹分析平台The animal is placed in the center of the apparatus and observed for a set time. Measurements compare the include total time spent in the open and closed arms (and central platform) as well as entries into the open and closed arms.6. 黑白箱实验(light dark box) The subject is placed in the dark portion of the box for a set period of acclimation time. At the end of this period, a door separating the two compartments is opened. The amount of time that the subject takes to emerge fully from the enclosed area into the open area is measured.
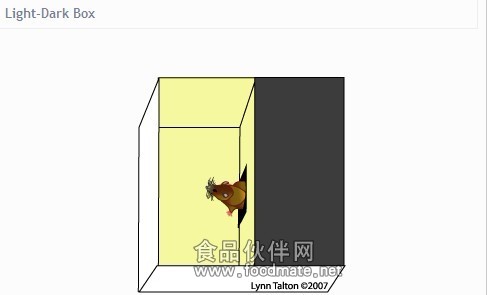 7. 社交行为实验(social interaction)SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统 The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time. A novel animal is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the novel animal is compared to the time spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with the same animal might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel animal. 7. 社交行为实验(social interaction)SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统 The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time. A novel animal is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the novel animal is compared to the time spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with the same animal might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel animal.  8. 条件性位置偏爱(Conditioned Place Preference) 条件性位置偏爱实验(CPP)实验是目前评价药物精神依赖性的经典实验模型。该实验将实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)置于条件性位置偏爱箱的白色观察区,并给予精神依赖药物然后观察实验动物在条件性位置偏爱箱的黑色区和白色区的活动情况,白色区、黑色区以及其中的灰*之间有小门可供动物自由穿梭。动物每次处于给药区就会在药物奖赏性效应的作用下对黑色和白*域产生位置上的偏好,其程度与药物的精神依赖性相关。 8. 条件性位置偏爱(Conditioned Place Preference) 条件性位置偏爱实验(CPP)实验是目前评价药物精神依赖性的经典实验模型。该实验将实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)置于条件性位置偏爱箱的白色观察区,并给予精神依赖药物然后观察实验动物在条件性位置偏爱箱的黑色区和白色区的活动情况,白色区、黑色区以及其中的灰*之间有小门可供动物自由穿梭。动物每次处于给药区就会在药物奖赏性效应的作用下对黑色和白*域产生位置上的偏好,其程度与药物的精神依赖性相关。 A drug is injected and the subject is introduced to distinctive environment A. This procedure is repeated for several trials. During these conditioning trials the animal develops an association between the subjective state produced by the drug (often drugs that produce mood elevation or euphoria in humans) and the contextual cues present while the drug is active. To test the conditioning, the animal is placed in an apparatus with drug-related cues in one compartment and neutral cues in the other. nbsp; If conditioning occurred, the animal will move toward the compartment containing the drug-related cues.In a Conditioned Place Preference experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with drug-related cues, and a compartment with neutral cues. If the conditioning was successful for positive, reinforcing drug states, they should spend more time in the A drug is injected and the subject is introduced to distinctive environment A. This procedure is repeated for several trials. During these conditioning trials the animal develops an association between the subjective state produced by the drug (often drugs that produce mood elevation or euphoria in humans) and the contextual cues present while the drug is active. To test the conditioning, the animal is placed in an apparatus with drug-related cues in one compartment and neutral cues in the other. nbsp; If conditioning occurred, the animal will move toward the compartment containing the drug-related cues.In a Conditioned Place Preference experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with drug-related cues, and a compartment with neutral cues. If the conditioning was successful for positive, reinforcing drug states, they should spend more time in the compartment with drug-related cues。In a Conditioned Place Aversion experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with an aversive stimulus, such as a shock; and a compartment with neutral cues. If the aversive conditioning was successful, they should spend more time in the compartment with neutral cues.9. 强迫游泳(force swim test)、悬尾实验(tail test)Since some mutations cause a deficit in swimming ability, the forced swim test can be used to demonstrate normal swimming and floating ability. The test is most frequently used to examine the "learned helplessness" response common in animal models of depression. compartment with drug-related cues。In a Conditioned Place Aversion experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with an aversive stimulus, such as a shock; and a compartment with neutral cues. If the aversive conditioning was successful, they should spend more time in the compartment with neutral cues.9. 强迫游泳(force swim test)、悬尾实验(tail test)Since some mutations cause a deficit in swimming ability, the forced swim test can be used to demonstrate normal swimming and floating ability. The test is most frequently used to examine the "learned helplessness" response common in animal models of depression.  The subject is suspended by the tail for a set interval the percentage of time the subject spends still versus moving is examined for evidence of the "learned helplessness" response common in models of depression.悬尾实验主要用于抗抑郁、镇静以及止痛类药物的研究。悬尾实验系统适用于大鼠、小鼠或其他实验室动物,通过固定动物尾部使其头向下悬挂,记录处于该环境的动物产生绝望的不动状态过程中的一系列参数。10. 条件性恐惧实验(fear conditioning)条件性恐惧分析用于小型啮齿类动物(大、小鼠)环境相关条件性恐惧实验研究。抗抑郁药和抗中枢兴奋药可以明 The subject is suspended by the tail for a set interval the percentage of time the subject spends still versus moving is examined for evidence of the "learned helplessness" response common in models of depression.悬尾实验主要用于抗抑郁、镇静以及止痛类药物的研究。悬尾实验系统适用于大鼠、小鼠或其他实验室动物,通过固定动物尾部使其头向下悬挂,记录处于该环境的动物产生绝望的不动状态过程中的一系列参数。10. 条件性恐惧实验(fear conditioning)条件性恐惧分析用于小型啮齿类动物(大、小鼠)环境相关条件性恐惧实验研究。抗抑郁药和抗中枢兴奋药可以明 显缩短不动状态持续的时间。实验过程中,实验对象被给与一个声音信号,随后给予电击刺激。该训练称为条件性训练,训练结束后实验动物进行声音信号或环境联系性实验。一般情况下啮齿类动物对相应的环境和不同环境下同样的声音信号都会做出明显的条件性恐惧反应,如静止不动。The Pavlovian Fear Conditioning task allows for the assessment of learning and memory regarding aversive events. The task allows for the simultaneous assessment of learning about simple, unimodal cues and learning about complex, multimodal stimuli such as context. Fear conditioning universally depends on the integrity of the amygdala, but context conditioning is sensitive to manipulations of the hippocampus. This task has been used extensively to demonstrate both genetically based impairments and enhancements in learning and memory.11. 震惊条件反射(startle and pre-pulse inhibition) 显缩短不动状态持续的时间。实验过程中,实验对象被给与一个声音信号,随后给予电击刺激。该训练称为条件性训练,训练结束后实验动物进行声音信号或环境联系性实验。一般情况下啮齿类动物对相应的环境和不同环境下同样的声音信号都会做出明显的条件性恐惧反应,如静止不动。The Pavlovian Fear Conditioning task allows for the assessment of learning and memory regarding aversive events. The task allows for the simultaneous assessment of learning about simple, unimodal cues and learning about complex, multimodal stimuli such as context. Fear conditioning universally depends on the integrity of the amygdala, but context conditioning is sensitive to manipulations of the hippocampus. This task has been used extensively to demonstrate both genetically based impairments and enhancements in learning and memory.11. 震惊条件反射(startle and pre-pulse inhibition) | Basic Startle Response | | In basic startle, startle stimuli of various intensities are presented unexpectedly. Varying startle response and habituation are recorded. | | Pre-Pulse Inhibition | In Pre-Pulse Inhibition (PPI), the startle stimulus is paired with a predictive cue. In normal subjects, the "pre-pulse" cue reduces the startle amplitude. This inhibition of the startle response is known as PPI. Humans and animal models of several disease states are known to have pre-pulse inhibition deficits, including schizophrenia, Alzheimer's, and PTSD. the "pre-pulse" cue reduces the startle amplitude. This inhibition of the startle response is known as PPI. Humans and animal models of several disease states are known to have pre-pulse inhibition deficits, including schizophrenia, Alzheimer's, and PTSD. | | Fear-Potentiated Startle | | In Fear-Potentiated Startle, the subjects are trained to associate a neutral stimulus, such as a light cue, with an aversive stimulus. When the startle response is tested in the presence of the light cue, the startle amplitude should be potentiated, or increased. | 12.新颖物体识别(novel object recognition)SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统 The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time. A novel object is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the new object is compared to the time spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with the same object might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel object.

|
 二、平台特性
二、平台特性 Morris水迷宫实验是一种强迫实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)游泳,学习寻找隐藏在水中平台的一种实验,Morris水迷宫主要用于测试实验动物对空间位置感和方向感(空间定位)的学习记忆能力,被广泛应用于学习记忆、老年痴呆、海马/外海马研究、智力与衰老、新药开发/筛选/评价、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学及行为生物学等多个学科的科学研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,在世界上已经得到广泛地认可,是医学院校开展行为学研究尤其是学习与记忆研究的经典实验。2. T迷宫实验(T-maze) T迷宫由1条干和2条臂构成。迷宫使动物在获取食物奖励时没有任何参考,只能根据自我判断选取食饵正确摆放一端。一般在测试前几天对其食量进行限制,测试前2天对动物进行训练。之后进行正式测试,每日连续测试15次,每次测试间隔1min,共3d。
Morris水迷宫实验是一种强迫实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)游泳,学习寻找隐藏在水中平台的一种实验,Morris水迷宫主要用于测试实验动物对空间位置感和方向感(空间定位)的学习记忆能力,被广泛应用于学习记忆、老年痴呆、海马/外海马研究、智力与衰老、新药开发/筛选/评价、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学及行为生物学等多个学科的科学研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,在世界上已经得到广泛地认可,是医学院校开展行为学研究尤其是学习与记忆研究的经典实验。2. T迷宫实验(T-maze) T迷宫由1条干和2条臂构成。迷宫使动物在获取食物奖励时没有任何参考,只能根据自我判断选取食饵正确摆放一端。一般在测试前几天对其食量进行限制,测试前2天对动物进行训练。之后进行正式测试,每日连续测试15次,每次测试间隔1min,共3d。  The T-maze is a choice task. The subject is placed in the base of the "T". Following a short delay, it is allowed to explore the maze and choose to enter either the right or left arms. The choice is scored according to variety of criterion, including spontaneous alternation, cued reward, or to indicate a preference. based on the criterion used in an experiment, the T-maze can be used to test learning and memory, preferences for stimuli or reward, or spontaneous alternation behavior.3. 八臂迷宫(Radial Arm Maze) Subjects are placed in the center of an eight-arm radial maze. Four randomly chosen arms are baited with food pellets in opaque containers. The subject is given the opportunity to visit all the arms and collect all the available food pellets.
The T-maze is a choice task. The subject is placed in the base of the "T". Following a short delay, it is allowed to explore the maze and choose to enter either the right or left arms. The choice is scored according to variety of criterion, including spontaneous alternation, cued reward, or to indicate a preference. based on the criterion used in an experiment, the T-maze can be used to test learning and memory, preferences for stimuli or reward, or spontaneous alternation behavior.3. 八臂迷宫(Radial Arm Maze) Subjects are placed in the center of an eight-arm radial maze. Four randomly chosen arms are baited with food pellets in opaque containers. The subject is given the opportunity to visit all the arms and collect all the available food pellets. After a rentention delay, the subject is returned to the maze. In win-stay conditions, the same four arms are baited, and the number of correct choices the subject makes in collecting the pellets is recorded. In win-shift conditions, the four arms NOT baited in the earlier trial are now baited, and the number of correct arm choices is recorded. Each day, a new set of four arms is chosen randomly.八臂迷宫用来检测药物或大脑受损状态下学习和记忆方面的表现,它由八个完全相同的臂组成,这些臂从一个中央平台放射出来,所以又被称为放射迷宫每个臂尽头有食物提供装置,根据分析动物取食的策略即进入每臂的次数、时间、正确次数、错误次数、路线等参数可以反映出实验动物的空间记忆能力。相对而言,八臂迷宫操作简便、可行,而且能区分短期的工作记忆和长期的参考记忆,现已被广泛用于学习记忆功能评价。 4. 自主活动、旷场实验(Open Field) The subject is placed in the activity chamber for a specified time period. Activity levels and movement in three
After a rentention delay, the subject is returned to the maze. In win-stay conditions, the same four arms are baited, and the number of correct choices the subject makes in collecting the pellets is recorded. In win-shift conditions, the four arms NOT baited in the earlier trial are now baited, and the number of correct arm choices is recorded. Each day, a new set of four arms is chosen randomly.八臂迷宫用来检测药物或大脑受损状态下学习和记忆方面的表现,它由八个完全相同的臂组成,这些臂从一个中央平台放射出来,所以又被称为放射迷宫每个臂尽头有食物提供装置,根据分析动物取食的策略即进入每臂的次数、时间、正确次数、错误次数、路线等参数可以反映出实验动物的空间记忆能力。相对而言,八臂迷宫操作简便、可行,而且能区分短期的工作记忆和长期的参考记忆,现已被广泛用于学习记忆功能评价。 4. 自主活动、旷场实验(Open Field) The subject is placed in the activity chamber for a specified time period. Activity levels and movement in three dimensions are recorded by the activity system and can be analyzed for evidence of hyperactiviy, hypoactivity, anxiety, explorative behaviors, and stereotyped rotation. 自发活动旷场旷场分析系统是观察研究实验动物神经精神变化、进入开阔环境后的各种行为,例如动物对新开阔环境的恐惧而主要在周边区域活动,在中央区域活动较少,但动物的探究特性又促使其产生在中央区域活动的动机,也可观察由此而产生的焦虑心理。中枢兴奋药物可以明显增加自主的活动而减少探究行为,一定剂量的抗精神病药物可以减少探究行为而不影响自主活动。5. 高架十字迷宫(Elevated Plus Maze) 高架十字迷宫是利用动物对新异环境的探究特性和对高悬敞开臂的恐惧形成矛盾冲突行为来考察动物的焦虑状态。高架十
dimensions are recorded by the activity system and can be analyzed for evidence of hyperactiviy, hypoactivity, anxiety, explorative behaviors, and stereotyped rotation. 自发活动旷场旷场分析系统是观察研究实验动物神经精神变化、进入开阔环境后的各种行为,例如动物对新开阔环境的恐惧而主要在周边区域活动,在中央区域活动较少,但动物的探究特性又促使其产生在中央区域活动的动机,也可观察由此而产生的焦虑心理。中枢兴奋药物可以明显增加自主的活动而减少探究行为,一定剂量的抗精神病药物可以减少探究行为而不影响自主活动。5. 高架十字迷宫(Elevated Plus Maze) 高架十字迷宫是利用动物对新异环境的探究特性和对高悬敞开臂的恐惧形成矛盾冲突行为来考察动物的焦虑状态。高架十 字迷宫具有一对开臂和一对闭臂,高架十字迷宫距离地面较高,相当于人站在峭壁上,使实验对象产生恐惧和不安心理。高架十字迷宫被广泛应用于新药开发、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学等多个学科的科学-研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,是医学院校与科研机构开展焦虑抑郁研究的经典实验。Xmaze 动物行为轨迹分析平台The animal is placed in the center of the apparatus and observed for a set time. Measurements compare the include total time spent in the open and closed arms (and central platform) as well as entries into the open and closed arms.6. 黑白箱实验(light dark box) The subject is placed in the dark portion of the box for a set period of acclimation time. At the end of this period, a door separating the two compartments is opened. The amount of time that the subject takes to emerge fully from the enclosed area into the open area is measured.
字迷宫具有一对开臂和一对闭臂,高架十字迷宫距离地面较高,相当于人站在峭壁上,使实验对象产生恐惧和不安心理。高架十字迷宫被广泛应用于新药开发、药理学、毒理学、预防医学、神经生物学、动物心理学等多个学科的科学-研究和计算机辅助教学等领域,是医学院校与科研机构开展焦虑抑郁研究的经典实验。Xmaze 动物行为轨迹分析平台The animal is placed in the center of the apparatus and observed for a set time. Measurements compare the include total time spent in the open and closed arms (and central platform) as well as entries into the open and closed arms.6. 黑白箱实验(light dark box) The subject is placed in the dark portion of the box for a set period of acclimation time. At the end of this period, a door separating the two compartments is opened. The amount of time that the subject takes to emerge fully from the enclosed area into the open area is measured. 7. 社交行为实验(social interaction)SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统 The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time. A novel animal is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the novel animal is compared to the time spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with the same animal might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel animal.
7. 社交行为实验(social interaction)SuperMaze动物行为学视频分析系统 The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time. A novel animal is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the novel animal is compared to the time spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with the same animal might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel animal.  8. 条件性位置偏爱(Conditioned Place Preference) 条件性位置偏爱实验(CPP)实验是目前评价药物精神依赖性的经典实验模型。该实验将实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)置于条件性位置偏爱箱的白色观察区,并给予精神依赖药物然后观察实验动物在条件性位置偏爱箱的黑色区和白色区的活动情况,白色区、黑色区以及其中的灰*之间有小门可供动物自由穿梭。动物每次处于给药区就会在药物奖赏性效应的作用下对黑色和白*域产生位置上的偏好,其程度与药物的精神依赖性相关。
8. 条件性位置偏爱(Conditioned Place Preference) 条件性位置偏爱实验(CPP)实验是目前评价药物精神依赖性的经典实验模型。该实验将实验动物(大鼠、小鼠)置于条件性位置偏爱箱的白色观察区,并给予精神依赖药物然后观察实验动物在条件性位置偏爱箱的黑色区和白色区的活动情况,白色区、黑色区以及其中的灰*之间有小门可供动物自由穿梭。动物每次处于给药区就会在药物奖赏性效应的作用下对黑色和白*域产生位置上的偏好,其程度与药物的精神依赖性相关。 A drug is injected and the subject is introduced to distinctive environment A. This procedure is repeated for several trials. During these conditioning trials the animal develops an association between the subjective state produced by the drug (often drugs that produce mood elevation or euphoria in humans) and the contextual cues present while the drug is active. To test the conditioning, the animal is placed in an apparatus with drug-related cues in one compartment and neutral cues in the other. nbsp; If conditioning occurred, the animal will move toward the compartment containing the drug-related cues.In a Conditioned Place Preference experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with drug-related cues, and a compartment with neutral cues. If the conditioning was successful for positive, reinforcing drug states, they should spend more time in the
A drug is injected and the subject is introduced to distinctive environment A. This procedure is repeated for several trials. During these conditioning trials the animal develops an association between the subjective state produced by the drug (often drugs that produce mood elevation or euphoria in humans) and the contextual cues present while the drug is active. To test the conditioning, the animal is placed in an apparatus with drug-related cues in one compartment and neutral cues in the other. nbsp; If conditioning occurred, the animal will move toward the compartment containing the drug-related cues.In a Conditioned Place Preference experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with drug-related cues, and a compartment with neutral cues. If the conditioning was successful for positive, reinforcing drug states, they should spend more time in the compartment with drug-related cues。In a Conditioned Place Aversion experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with an aversive stimulus, such as a shock; and a compartment with neutral cues. If the aversive conditioning was successful, they should spend more time in the compartment with neutral cues.9. 强迫游泳(force swim test)、悬尾实验(tail test)Since some mutations cause a deficit in swimming ability, the forced swim test can be used to demonstrate normal swimming and floating ability. The test is most frequently used to examine the "learned helplessness" response common in animal models of depression.
compartment with drug-related cues。In a Conditioned Place Aversion experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with an aversive stimulus, such as a shock; and a compartment with neutral cues. If the aversive conditioning was successful, they should spend more time in the compartment with neutral cues.9. 强迫游泳(force swim test)、悬尾实验(tail test)Since some mutations cause a deficit in swimming ability, the forced swim test can be used to demonstrate normal swimming and floating ability. The test is most frequently used to examine the "learned helplessness" response common in animal models of depression.
 The subject is suspended by the tail for a set interval the percentage of time the subject spends still versus moving is examined for evidence of the "learned helplessness" response common in models of depression.悬尾实验主要用于抗抑郁、镇静以及止痛类药物的研究。悬尾实验系统适用于大鼠、小鼠或其他实验室动物,通过固定动物尾部使其头向下悬挂,记录处于该环境的动物产生绝望的不动状态过程中的一系列参数。10. 条件性恐惧实验(fear conditioning)条件性恐惧分析用于小型啮齿类动物(大、小鼠)环境相关条件性恐惧实验研究。抗抑郁药和抗中枢兴奋药可以明
The subject is suspended by the tail for a set interval the percentage of time the subject spends still versus moving is examined for evidence of the "learned helplessness" response common in models of depression.悬尾实验主要用于抗抑郁、镇静以及止痛类药物的研究。悬尾实验系统适用于大鼠、小鼠或其他实验室动物,通过固定动物尾部使其头向下悬挂,记录处于该环境的动物产生绝望的不动状态过程中的一系列参数。10. 条件性恐惧实验(fear conditioning)条件性恐惧分析用于小型啮齿类动物(大、小鼠)环境相关条件性恐惧实验研究。抗抑郁药和抗中枢兴奋药可以明 显缩短不动状态持续的时间。实验过程中,实验对象被给与一个声音信号,随后给予电击刺激。该训练称为条件性训练,训练结束后实验动物进行声音信号或环境联系性实验。一般情况下啮齿类动物对相应的环境和不同环境下同样的声音信号都会做出明显的条件性恐惧反应,如静止不动。The Pavlovian Fear Conditioning task allows for the assessment of learning and memory regarding aversive events. The task allows for the simultaneous assessment of learning about simple, unimodal cues and learning about complex, multimodal stimuli such as context. Fear conditioning universally depends on the integrity of the amygdala, but context conditioning is sensitive to manipulations of the hippocampus. This task has been used extensively to demonstrate both genetically based impairments and enhancements in learning and memory.11. 震惊条件反射(startle and pre-pulse inhibition)
显缩短不动状态持续的时间。实验过程中,实验对象被给与一个声音信号,随后给予电击刺激。该训练称为条件性训练,训练结束后实验动物进行声音信号或环境联系性实验。一般情况下啮齿类动物对相应的环境和不同环境下同样的声音信号都会做出明显的条件性恐惧反应,如静止不动。The Pavlovian Fear Conditioning task allows for the assessment of learning and memory regarding aversive events. The task allows for the simultaneous assessment of learning about simple, unimodal cues and learning about complex, multimodal stimuli such as context. Fear conditioning universally depends on the integrity of the amygdala, but context conditioning is sensitive to manipulations of the hippocampus. This task has been used extensively to demonstrate both genetically based impairments and enhancements in learning and memory.11. 震惊条件反射(startle and pre-pulse inhibition) the "pre-pulse" cue reduces the startle amplitude. This inhibition of the startle response is known as PPI. Humans and animal models of several disease states are known to have pre-pulse inhibition deficits, including schizophrenia, Alzheimer's, and PTSD.
the "pre-pulse" cue reduces the startle amplitude. This inhibition of the startle response is known as PPI. Humans and animal models of several disease states are known to have pre-pulse inhibition deficits, including schizophrenia, Alzheimer's, and PTSD.





